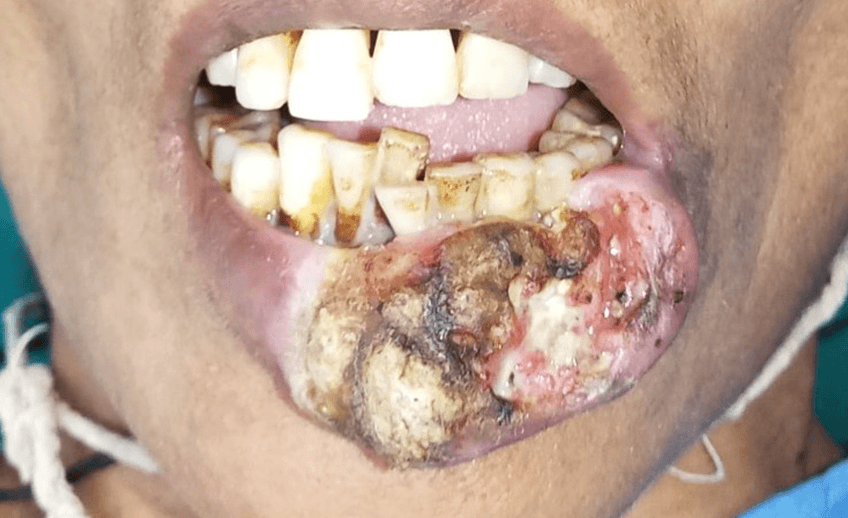
Orofacial cancers are cancers that affect the oral and/or facial tissues. They may involve the
tongue, lips, floor of mouth, jaws, salivary glands, cheeks, hard and soft palate, etc. Oral
cancer appears as a growth or sore in mouth that does not go away. It can be life threatening if
not diagnosed and treated early.
The most common symptoms of Orofacial cancer:
- Swellings/thickenings, lumps or bumps, rough spots/crusts/or eroded areas on the lips, gums, or other areas inside the mouth.
- The development of velvety white, red or spekled (white and red) patches in the mouth.
- Unexplained bleeding in the mouth
- Unexplained numbness, loss of felling or pain /tenderness in any area of face, mouth or neck.
- Persistent sore on the face, neck or mouth that bleeds easily and do not heal within 2 weeks.
- Soreness or felling that something is caught in the back of throat.
- Difficulty in chewing or swallowing, speaking or moving the jaws or tongue.
- A change in the way your teeth or dentures fit together.
- Dramatic weight loss
The management of Orofacial cancer depends on the stage at which it is diagnosed. Thus, if you notice any of the above signs, it is best to visit your Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon for an opinion. A biopsy often confirms the diagnosis and further treatment includes removal of the lesion with removal of the associated lymph nodes. Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy may also be required for some patients.